Dear farmer and breeder, today I would like to inform and remind each other about some cattle diseases. Today we will look at and discuss one of the two diseases CATTLE WORMS. Worm disease causes losses to cattle breeders. Research shows that many cattle are affected by the worms and reduce production. In addition, research shows that the problem of worms in cattle is widespread . (i) SPECIES OF WORMS. Worms that affect cattle are divided into different groups as follows; Liver flukes. Worms that end up in the lungs…
Author: Mshindo Media
FOWL POX DISEASE/POX
This is one of the viral diseases that have been attacking chickens to a large extent. Source 👉This disease is caused by a virus, Fowl Pox Virus This virus affects chickens of all ages, large and small Spreading 👉This disease spreads very quickly in the environment or shed immediately after entering 👉For other areas, with many mosquitoes, it is said that piaa is spread by mosquitoes. 👆 This disease is also hidden or carried by other birds, especially ducks and sent to chickens. Treatment 👉 There is no cure for…
PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF FOWL POX I Mshindo Media
Several diseases which are easily vaccinated against need to be considered in their health management programs like fowl pox disease. Fowl Pox is a relatively spreading viral infection of chickens characterized by scab-like lesions on the skin of the unfeathered body parts and/or diphtheritic (wet) membranes lining the mouth or air passages. Infection with the fowl pox virus will cause the chickens to have -Poor growth, -Poor feed conversion and a -Precipitous fall in egg production. Mortality rate will be marked if the lesions are limited to the skin,death may…
How can you control disease in broiler chicken I Mshindo Media
Prevention and Control of disease in broiler chicken In poultry industry primarily emphasis is given more on prevention and control than curative measures. A suggestive disease prevention & control programme follows: · Start with disease free stock. · V accine chicks against Ranikhet & Merek’s disease at Hatchery . · Use coccidiostal to prevent coccidiosis.…
Salmonella in poultry I Mshindo Media
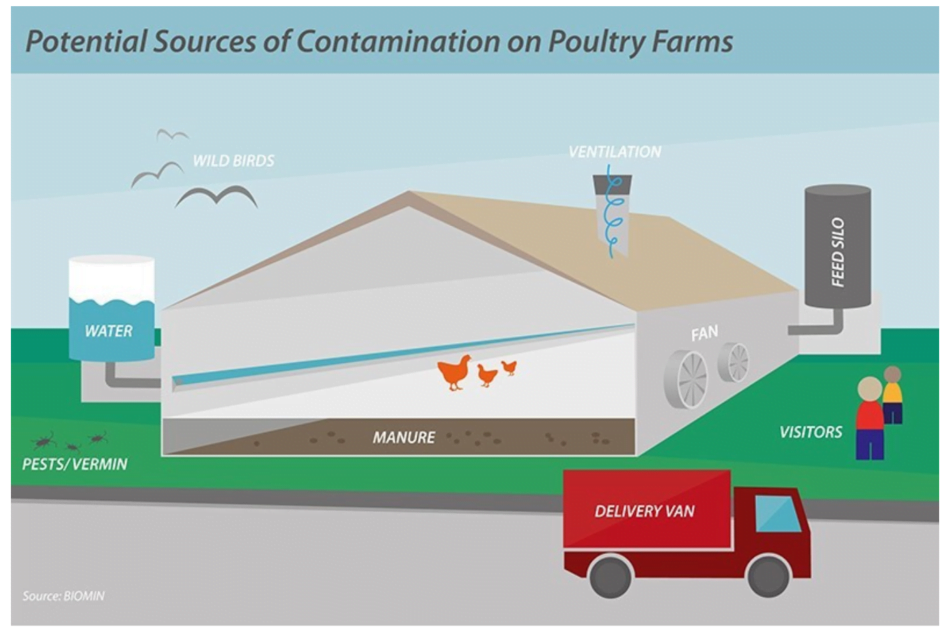
Basically, salmonella is a faecal-oral infection. Infected birds can clear themselves of infection after some time, but some excrete bacteria in droppings for several months. It is practically impossible to rid a salmonella infected flock from the infection when kept on permanent beddingSalmonella in poultry can be regarded as two types of infection: the first is primarily of importance for public health (what we usually call “salmonella” and which may cause illness in man). Salmonella in humans is from an international perspective often linked to the consumption of eggs, meat or…
Salmonellosis in Poultry I Mshindo Media
Signs, causes, treatment and prevention of Salmonella infection in chickens and other avian species Salmonella is an enteric pathogen that can infect almost all animals, including humans. Salmonellosis in poultry is caused by Gram-negative bacteria from the genus Salmonella. There are only two species in this genus, enterica and bongori (Lin-Hui and Cheng-Hsun, 2007), but almost 2,700 serotypes (serovars), of which around 10% have been isolated from birds. In general, most serotypes of Salmonella can infect several animal species (Gast, 2008), such as Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis. Food safety and Salmonella in poultry Food safety is a key topic when it…
Feeding Guides for Broiler Chickens
How much water do your chicks need? Make sure your chicken always have water. Without enough water they will not grow well. For each 1 g of feed, your chicks need 2 g of water. For the first 3-5 days, add to the water: Clean the drinkers every day. Feeding guide for your broilers In order to have a healthy and strong flock of broilers, make sure you follow this feeding guide using Unga Farmcare EA feeds: Change feed slowly: When chicks are out of the brooder, remove feeding trays. Hang the feeders from…
The history of animal breeding
There are 5 very important aspects that should be considered in animal breeding: Definitions A trait is “a distinguishing phenotypic characteristic, typically belonging to an individual”. In practice this means anything you can record or measure on an individual. A phenotype is that what you observe or measure on the animal for a certain trait. It can depend both on the genetic background of the animal (provided it is heritable) and external circumstances such as level of nutrition Heritable traits Being able to predict the success of animal breeding relies on one very important factor that we…
Poultry Farming
Introduction to Animal Husbandry If we talk about agriculture, animal husbandry has its own importance for raising livestock in a scientific way i.e by giving a proper environment to the cattle. In such an environment, cattle remain disease-free and healthy from both inside and out. Animal husbandry is considered important as this process allows us to increase livestock production to cover up the demands of human beings tremendously increasing in population. As due to the increase in population demands of egg, meat, milk is also increasing day by day, so…
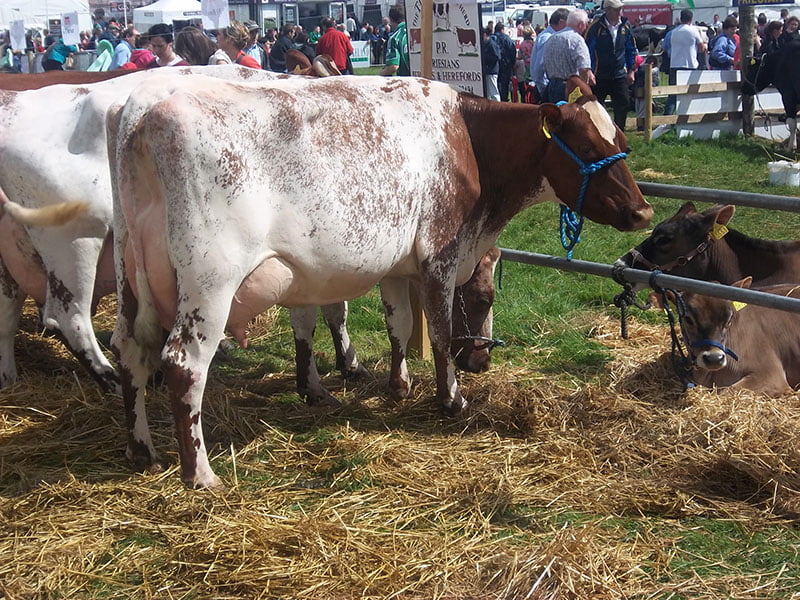
Diseases affecting dairy cows
There are a range of diseases affecting dairy cows with different impacts on welfare, productivity and profitability, so it makes sense to have a good understanding of common conditions. The list of potential diseases affecting dairy cows is almost endless with some diseases more significant than others. Diseases may compromise animal welfare, limit productivity or add additional costs to your business. The relative impact of different diseases depends on the health status of your herd so it is advisable to work with your vet to assess your own situation. Below…
Animal Breeding
Objective and Methods of Animal Breeding Animal breeding is when animals produce improved breeds of domesticated animals by improving their genotypes and physiology through selective mating by descent, similar in most characters like general appearance, features, size and configuration. Objectives of Animal Breeding Improved growth rate Increased production of milk, meat, egg, wool Superior quality of milk, meat, eggs, wool Improved resistance to various diseases Increased productive life Increased or, at least, acceptable reproduction rate Methods of Animal Breeding 1.Inbreeding Breeding that occurs between animals of the same breed for…
Mastitis Prevention and Treatment
Mastitis Prevention and Treatment The most costly dairy industry disease, mastitis, creates problems that affect the animal, finances, and food safety. When evaluating the expenses associated with mastitis, dairy clients need to keep in mind that the financial loss associated with treating the disease extends beyond the cost of prevention.Below is information you can give to your dairy clients to help: Calculating the Costs of Mastitis Running a dairy is a business. When balancing the cost of prevention versus the cost of treatment, the final decision has to be economically valid.…
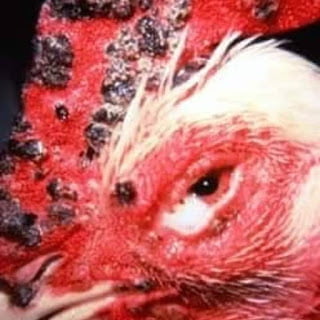
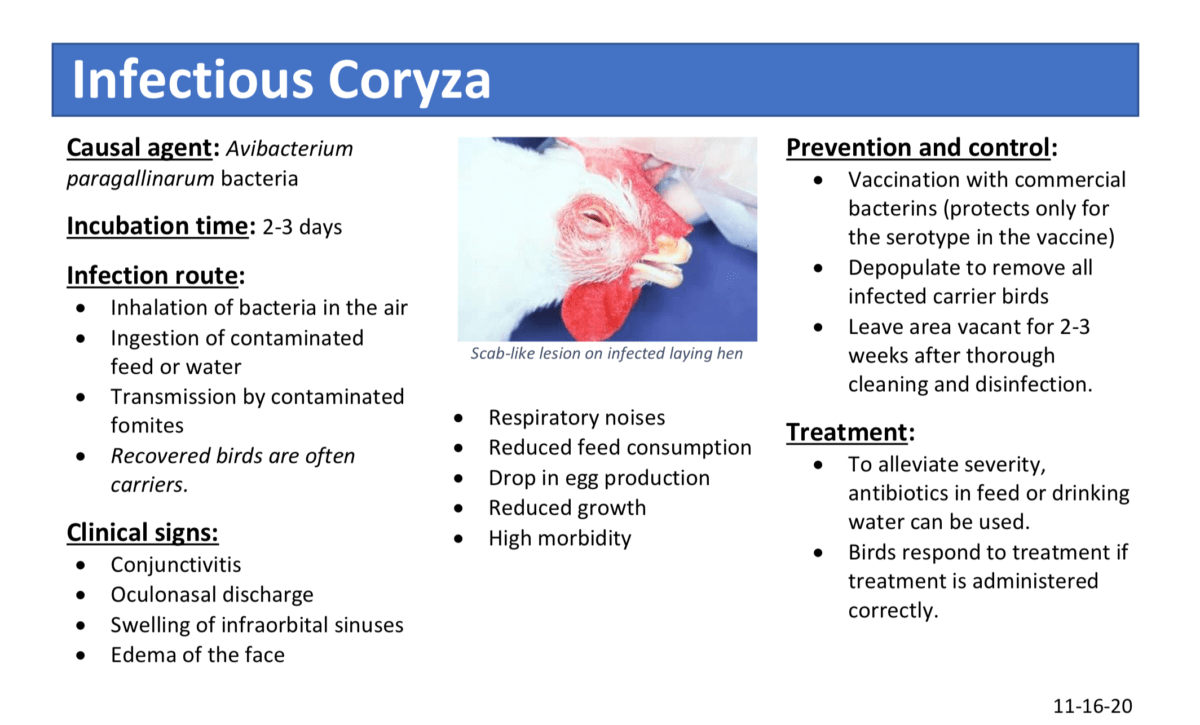
INFECTIOUS CORYZA
INFECTIOUS CORYZA Coryza is the medical term for local cold.However its more serious in chicken.Its airbone disease,Can be passed from bird to bird,through infected droplets,contaminated feeds,water,beddings and dust particles.Birds are also highly susceptible at places such as poultry shows,swap meet and live birds market place or all places where they can be in contact with infected birds.It can also spread via wild birds so try to keep them out of the chicken area as much as possible.Poor unsanitary housing and overcrowding exacerbates the problem since the bacteria can proliferate in…
Bleeding calf syndrome
Bleeding calf syndrome (Bovine neonatal pancytopenia) results in unexplained bleeding or haemorrhaging from the skin, nares, mouth, rectum and injection sites and ear tags and with a raised temperature in some cases. Clinical signs There have been different clinical manifestations seen, ranging from calves being found dead to unexpected excessive bleeding with secondary infection and malaise and on post mortem areas of bleeding or haemorrhage are seen throughout the carcase. The bone marrow also shows damage (aplasia) indicating that there is a problem with producing factors involved in blood clotting.…
Milking Procedures
Consistency in management and proper milking procedures are essential for profitable dairy production. Following correct procedures can lead to increased production along with quicker milk output and quality milk. The following procedures are suggested to increase quality and production while decreasing parlor or tie-stall milking times: Clean Teats as necessary ᵃ Completely coat each teat to the base of the udder with an effective teat disinfectant Observe the foremilk by stripping milk into a strip cup (not under the cow). This is known as fore-stripping (may be done before pre-…
Bluetongue
Bluetongue is a non-contagious, viral disease affecting domestic and wild ruminants (primarily sheep and including cattle and goats), that is transmitted by insects, particularly biting midges. The severity of disease varies among different species with symptoms being most severe in sheep resulting in death, weight loss and disruption in wool growth. In highly susceptible sheep, morbidity can be as high as 100%. Mortality averages from 2-30% but can be as high as 70%. Cattle often have a higher infection rate than sheep and demonstration and severity of clinical signs varies…
Broiler Management
BroilerIt is a bird of about 8 weeks of age of either sex (straight-run chicks) with an average body weight of 1.5 to 2.0 kg with a flexible breast bone cartilage, pliable and tender meat. Housing systemsBroilers can be housed on deep-litter, slatted or wire floor or cages. However, cage, slat and wire floor rearing of broilers are not as popular as litter floor rearing, due to problems like breast blisters, leg weakness and higher initial investment. Rearing systemsThe systems of rearing refer to either single batch at a time…
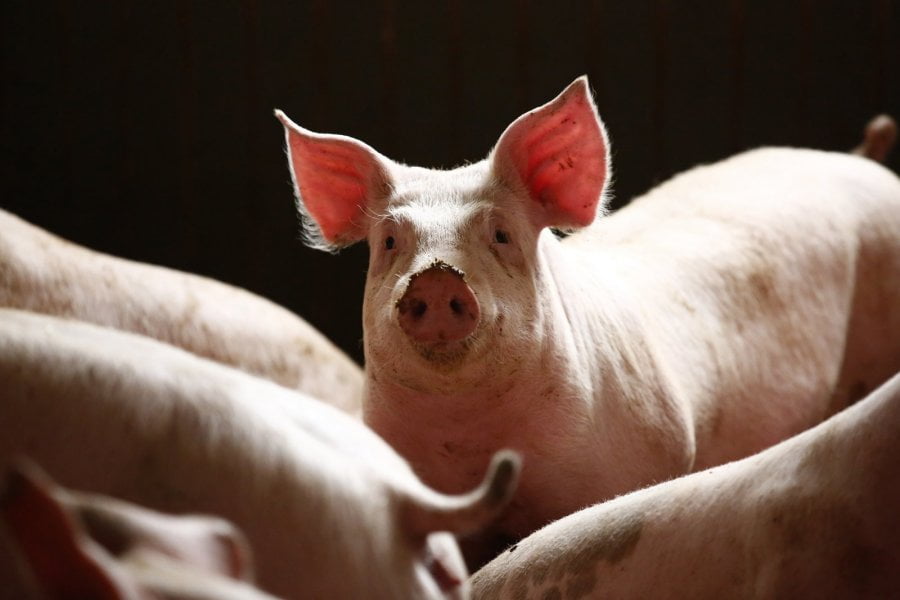
Pig Management – Birth to Weaning
Good care and management in the farrowing quarters has a major influence on the number of liveborn piglets that are weaned and on how well they perform in later stages of production. According to a 1995 survey of swine management practices in the United States, the average number of preweaning piglet deaths per litter on farms was .88 or 9.4% of those born alive. The two leading causes of preweaning deaths were laid on (48.7%) and starvation (20.5%). Other surveys have shown that over 50% of the deaths occur in…