Milk fever Milk fever arises when cows are unable to mobilise sufficient calcium at calving. This website is intended to provide a better understanding of the challenge of controlling (sub)clinical milk fever for dairy farmers. What is milk fever? Milk fever, or hypocalcemia, is a calcium deficiency. The disease has a clinical and a subclinical form and affects when cows they are at their most vulnerable – during the transition period. Cows need a large amount of calcium immediately after calving: initially they take the calcium from their blood and…
Category: Animal Health
Common Cattle diseases I Signs,Prevention and their management
COMMON CATTLE DISEASES Cattle suffer from a variety of diseases. Diseases are more common among herds kept in tight quarters, such as on feedlots, or large herds kept on too few acres. Diseases are also more common among stressed animals, such as calves weaned and shipped immediately to new locations. Keeping new animals quarantined until you’re sure they aren’t suffering from disease is a simple herd management practice that can keep the majority of your livestock healthy by reducing the number of potentially transmitted diseases. Beef cattle diseases fall into…
Disease Treatment, Control & Prevention (Ticks, Wounds,Vaccination)
Prevention of diseases is always both better and cheaper than treatment. Even if vaccines and other preventive measures may seem expensive, they are in the long run much cheaper than loosing animals or letting animals suffer and loose condition and buying expensive drugs – not to mention the fees of the vets. The following public and private disease prevention measures also protects the rights of the animals to a worthy enjoyable life and are the pillars of good and successful management. Hygiene / Insect and Tick control Many serious diseases are transferred…
Mastitis prevention control and Treatment
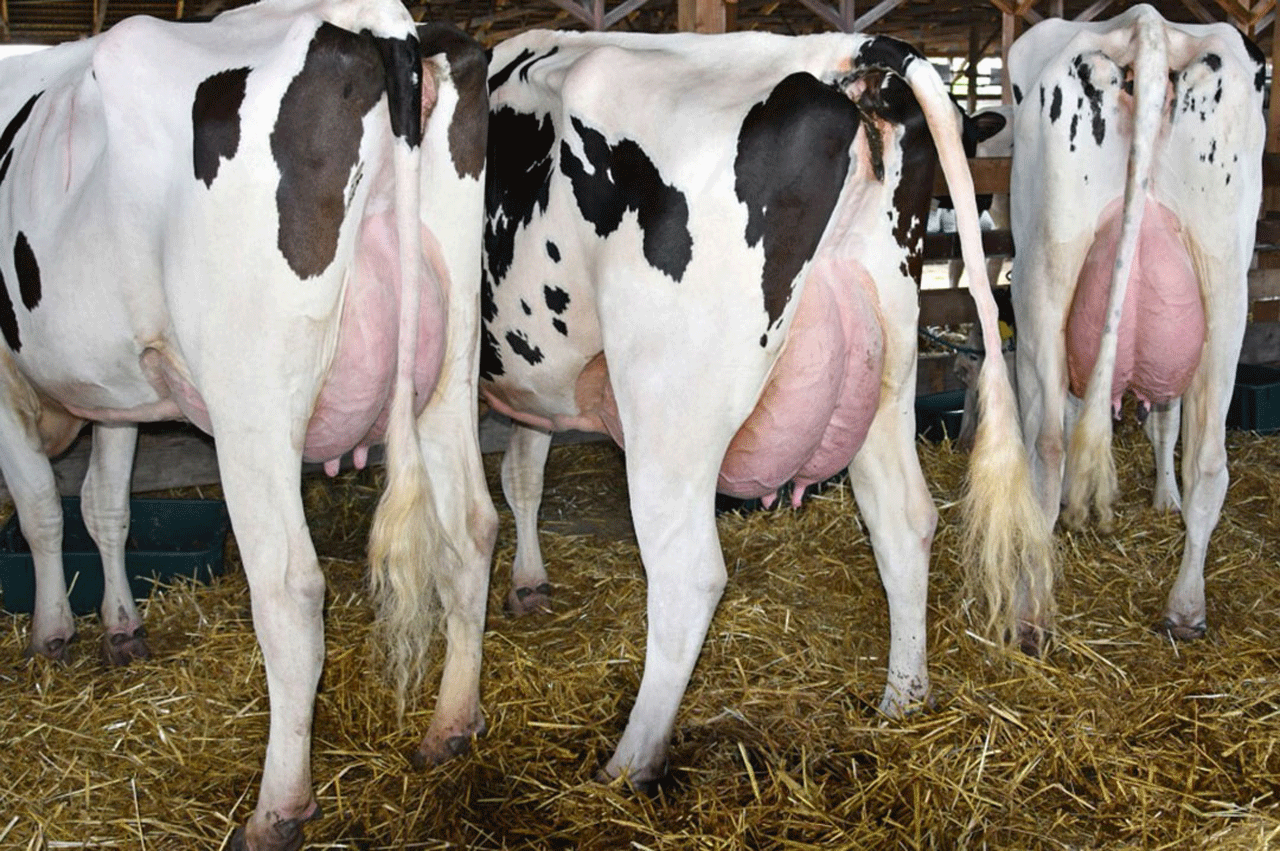
What is mastitis in cattle? Mastitis is an inflammation of the mammary gland or udder. Mastitis in dairy cows is caused by udder infections, usually resulting from bacteria introduced either during the milking process or from environmental contact. What antibiotics are used to treat mastitis in cows? The drugs considered include the more common penicillins, aminoglycosides and macrolides; oxytetracyline, chloramphenicol, trimethoprim, and several sulphonamides. The success of systemic therapy against mastitis depends to a large extent on the concentration of antibacterial drug achieved at foci of infection. What is the best treatment for mastitis in cows?Treatment approachStripping (hand milking) out the infected milk…
Cattle diseases I Mshindo Media
Dear farmer and breeder, today I would like to inform and remind each other about some cattle diseases. Today we will look at and discuss one of the two diseases CATTLE WORMS. Worm disease causes losses to cattle breeders. Research shows that many cattle are affected by the worms and reduce production. In addition, research shows that the problem of worms in cattle is widespread . (i) SPECIES OF WORMS. Worms that affect cattle are divided into different groups as follows; Liver flukes. Worms that end up in the lungs…
FOWL POX DISEASE/POX
This is one of the viral diseases that have been attacking chickens to a large extent. Source 




PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF FOWL POX I Mshindo Media
Several diseases which are easily vaccinated against need to be considered in their health management programs like fowl pox disease. Fowl Pox is a relatively spreading viral infection of chickens characterized by scab-like lesions on the skin of the unfeathered body parts and/or diphtheritic (wet) membranes lining the mouth or air passages. Infection with the fowl pox virus will cause the chickens to have -Poor growth, -Poor feed conversion and a -Precipitous fall in egg production. Mortality rate will be marked if the lesions are limited to the skin,death may…
Salmonella in poultry I Mshindo Media
Basically, salmonella is a faecal-oral infection. Infected birds can clear themselves of infection after some time, but some excrete bacteria in droppings for several months. It is practically impossible to rid a salmonella infected flock from the infection when kept on permanent beddingSalmonella in poultry can be regarded as two types of infection: the first is primarily of importance for public health (what we usually call “salmonella” and which may cause illness in man). Salmonella in humans is from an international perspective often linked to the consumption of eggs, meat or…
Diseases affecting dairy cows
There are a range of diseases affecting dairy cows with different impacts on welfare, productivity and profitability, so it makes sense to have a good understanding of common conditions. The list of potential diseases affecting dairy cows is almost endless with some diseases more significant than others. Diseases may compromise animal welfare, limit productivity or add additional costs to your business. The relative impact of different diseases depends on the health status of your herd so it is advisable to work with your vet to assess your own situation. Below…
Mastitis Prevention and Treatment
Mastitis Prevention and Treatment The most costly dairy industry disease, mastitis, creates problems that affect the animal, finances, and food safety. When evaluating the expenses associated with mastitis, dairy clients need to keep in mind that the financial loss associated with treating the disease extends beyond the cost of prevention.Below is information you can give to your dairy clients to help: Calculating the Costs of Mastitis Running a dairy is a business. When balancing the cost of prevention versus the cost of treatment, the final decision has to be economically valid.…
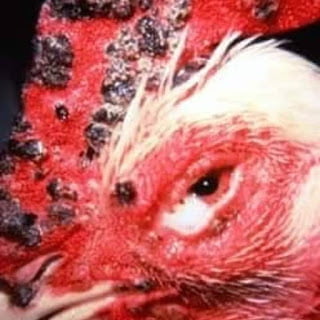
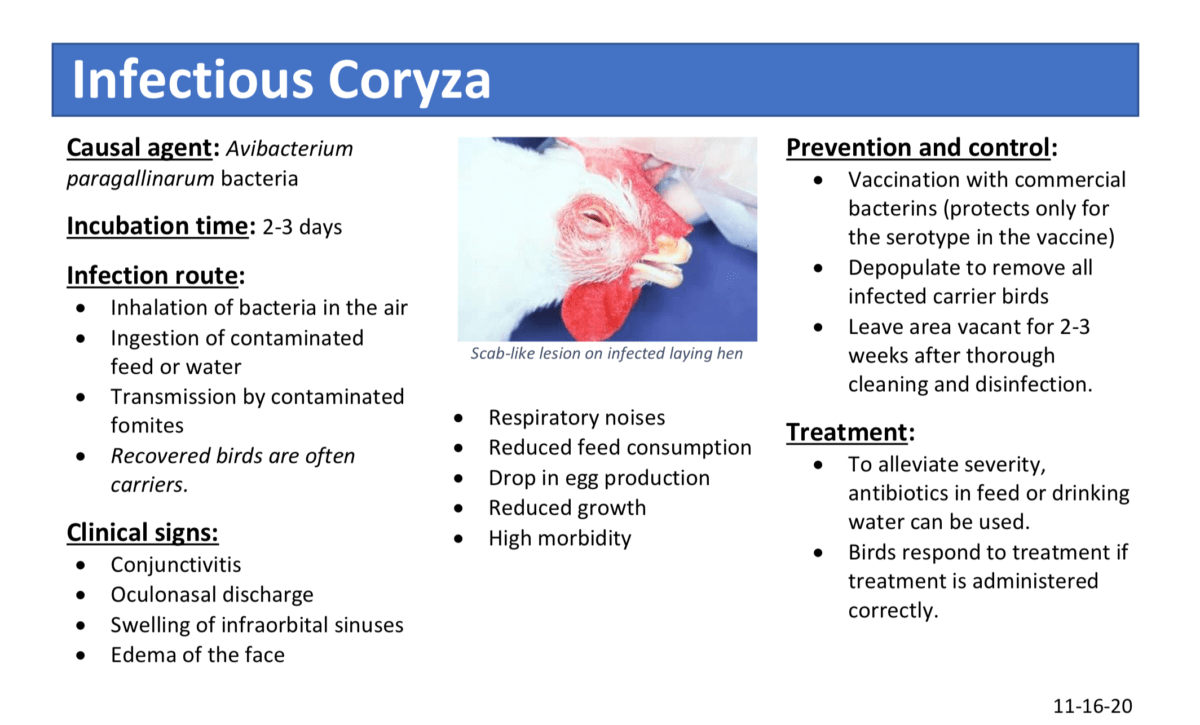
INFECTIOUS CORYZA
INFECTIOUS CORYZA Coryza is the medical term for local cold.However its more serious in chicken.Its airbone disease,Can be passed from bird to bird,through infected droplets,contaminated feeds,water,beddings and dust particles.Birds are also highly susceptible at places such as poultry shows,swap meet and live birds market place or all places where they can be in contact with infected birds.It can also spread via wild birds so try to keep them out of the chicken area as much as possible.Poor unsanitary housing and overcrowding exacerbates the problem since the bacteria can proliferate in…
Bleeding calf syndrome
Bleeding calf syndrome (Bovine neonatal pancytopenia) results in unexplained bleeding or haemorrhaging from the skin, nares, mouth, rectum and injection sites and ear tags and with a raised temperature in some cases. Clinical signs There have been different clinical manifestations seen, ranging from calves being found dead to unexpected excessive bleeding with secondary infection and malaise and on post mortem areas of bleeding or haemorrhage are seen throughout the carcase. The bone marrow also shows damage (aplasia) indicating that there is a problem with producing factors involved in blood clotting.…
Bluetongue
Bluetongue is a non-contagious, viral disease affecting domestic and wild ruminants (primarily sheep and including cattle and goats), that is transmitted by insects, particularly biting midges. The severity of disease varies among different species with symptoms being most severe in sheep resulting in death, weight loss and disruption in wool growth. In highly susceptible sheep, morbidity can be as high as 100%. Mortality averages from 2-30% but can be as high as 70%. Cattle often have a higher infection rate than sheep and demonstration and severity of clinical signs varies…